HOT100
哈希
P1 两数之和
java
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[] {map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}P49 字母异位词分组
java
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] cnt = new char[26];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
cnt[str.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
String temp = new String(cnt);
if (!map.containsKey(temp)) {
map.put(temp, new ArrayList<>());
}
map.get(temp).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}P128 最长连续序列
解法一
- 使用 set 去重
- 遍历集合,如果元素是区间的第一个元素,即 set.contains(num - 1),则循环获取区间长度
- 由于每个元素只会遍历一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n)
java
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int max = 0;
for (int num : set) {
if (!set.contains(num - 1)) {
int currentNum = num;
int count = 1;
while (set.contains(currentNum + 1)) {
currentNum += 1;
count += 1;
}
max = Math.max(max, count);
}
}
return max;
}解法二:动态规划
java
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
// 表示 key 包含在区间中的最长长度
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int max = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
// 不存在哈希表中,说明num第一次出现,因此num-1必为右端点,num+1必为左端点
if (!map.containsKey(num)) {
Integer leftLen = map.getOrDefault(num - 1, 0);
Integer rightLen = map.getOrDefault(num + 1, 0);
int length = 1 + leftLen + rightLen;
max = Math.max(length, max);
map.put(num, length);
map.put(num - leftLen, length);
map.put(num + rightLen, length);
}
}
return max;
}双指针
P283 移动零
java
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while (right < nums.length) {
if (nums[right] != 0) {
nums[left++] = nums[right++];
} else {
right++;
}
}
while (left < nums.length) {
nums[left++] = 0;
}
}P11 盛水最多的容器
java
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int left = 0, right = height.length - 1;
int max = 0;
while (left < right) {
int area = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);
max = Math.max(max, area);
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
return max;
}P15 三数之和
- 排序数组
- 固定 first,枚举 second,由于数组升序,当 second 不断增加,third 会不断减少,由于单调性,固定 first 时,second ~ n 每个元素只会遍历一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n^2)
- 为了保证不重复,枚举的值需要与前一个值不同
java
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// 枚举 a
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
// 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
// c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
// 枚举 b
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
// 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums[first]);
list.add(nums[second]);
list.add(nums[third]);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}P42 接雨水
java
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int leftMax = height[left], rightMax = height[right];
left++;
right--;
int sum = 0;
// 计算每一列能存储的雨水相加
while (left <= right) {
leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, height[left]);
rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, height[right]);
if (leftMax < rightMax) {
sum += leftMax - height[left++];
} else {
sum += rightMax - height[right--];
}
}
return sum;
}滑动窗口
P3 无重复字符的最长子串
java
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int[] cnt = new int[258];
int ans = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
cnt[c]++;
if (cnt[c] > 1) {
ans = Math.max(right - left, ans);
while (cnt[c] > 1) {
cnt[s.charAt(left++)]--;
}
}
right++;
}
ans = Math.max(right - left, ans);
return ans;
}P438 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
java
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
if(s.length() < p.length()) return new ArrayList<>();
int[] cnt = new int[26];
for (char c : p.toCharArray()) {
cnt[c - 'a']++;
}
int[] counts = new int[26];
int left = 0, right = p.length();
for (int i = 0; i < p.length(); i++) {
counts[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (right < s.length()) {
if (Arrays.equals(counts, cnt)) {
ans.add(left);
}
counts[s.charAt(left++) - 'a']--;
counts[s.charAt(right++) - 'a']++;
}
if(Arrays.equals(counts, cnt)) ans.add(left);
return ans;
}java
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] need = new int[26];
int[] windows = new int[26];
int needNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < p.length(); i++) {
int idx = p.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (need[idx] == 0)
needNum++;
need[idx]++;
}
// aabaa ab
int count = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
int idx_r = s.charAt(right) - 'a';
windows[idx_r]++;
if (need[idx_r] == windows[idx_r]) {
count++;
}
while (right - left + 1 >= p.length()) {
if (count == needNum) {
res.add(left);
}
int idx_l = s.charAt(left) - 'a';
if (need[idx_l] == windows[idx_l]) {
count--;
}
windows[idx_l]--;
left++;
}
right++;
}
return res;
}子串
和为 k 的子数组
解法:利用前缀和性质得到公式 pre[j - 1] = pre[i] - k,利用哈希表存储前缀和的个数即可
java
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
// key: 前缀和 value: 下标个数
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0, sum = 0;
map.put(0, 1);
// pre[i] - pre[j - 1] = k
// pre[j - 1] = sum - k;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) {
count += map.get(sum - k);
}
map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}滑动窗口最大值
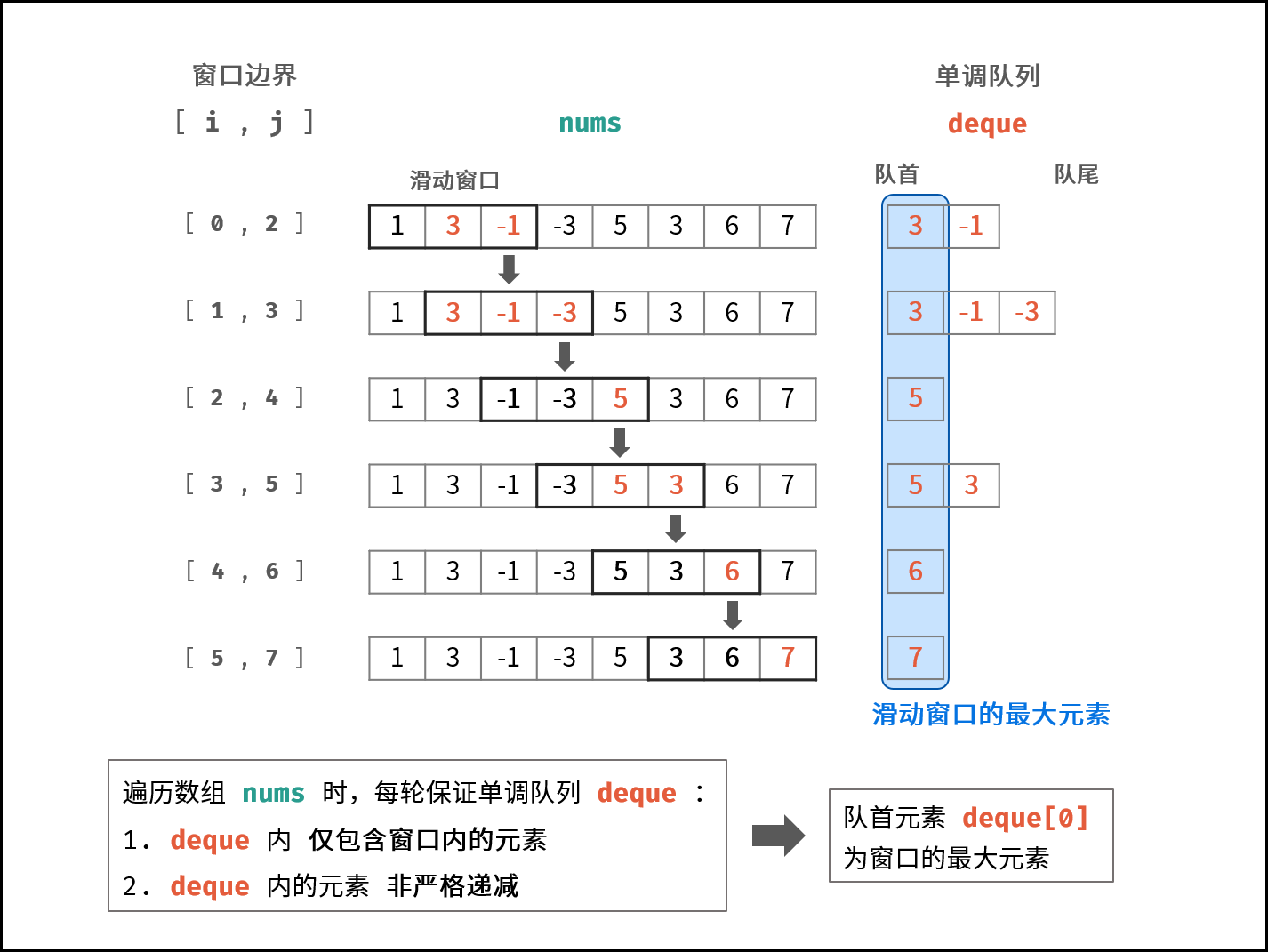
java
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 保证队列非严格递减
while (!queue.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[queue.peekLast()]) {
queue.pollLast();
}
queue.offerLast(i);
// 超出窗口大小,弹出队列
if (queue.peekFirst() < i - k + 1) {
queue.pollFirst();
}
// 形成第一个窗口
if (i >= k - 1) {
res[index++] = nums[queue.peekFirst()];
}
}
return res;
}矩阵
P48 旋转图像
java
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
// 上下翻转
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - 1 -i][j];
matrix[n - 1 -i][j] = tmp;
}
}
// 左斜对角线(\)翻转
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 第二层遍历终止条件为 j < i
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
int tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}P240 搜索二维矩阵 II
java
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int n = matrix.length, m = matrix[0].length;
int i = 0, j = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (i < n && j >= 0) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
j--;
} else if (matrix[i][j] < target) {
i++;
}
}
return false;
}链表
P160 相交链表
pA 和 pB 遍历到末尾时重新遍历另一条链表以消除长度差
java
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}P234 回文链表
- 慢指针反转前半段链表
- 遍历前半段和后半段链表是否一致
java
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = pre;
pre = slow;
slow = next;
}
// 奇数节点
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (slow != null) {
if (slow.val != pre.val) return false;
slow = slow.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return true;
}P141 环形链表
java
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}P142 环形链表 II
第一次相遇到环点距离等于头节点到环点距离 证明:
- 环点前有 a 个节点,环有 b 个节点
- 第一次相遇:f = 2s,f = s + nb,得到:f = 2nb,s = nb,到达环点的步数为 a + nb
- 第二次相遇:让 slow 到达头节点,s = a,f = a + nb 时相遇,此时为环点
java
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}P25 k 个一组翻转链表
java
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode end = dummy;
while (end.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) end = end.next;
if (end == null) break;
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
// 前一个节点的 next 为翻转后的头节点
pre.next = reverse(start);
// 拼接下一个翻转链表
start.next = next;
// 更新 pre, end, 开始下一次
pre = start;
end = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// head ~ null 翻转, 返回最后一个节点
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}java
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode currentNode = head;
int nodeCount = 0;
// 计算链表长度
while (currentNode != null) {
nodeCount++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 剩余节点不足k个 直接返回头节点
if (nodeCount < k) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
head.next = reverseKGroup(cur, k);
return pre;
}P148 排序链表
为了找到左部分的最后节点并让 slow.next = null,需要 fast = head.next
java
// 递归归并
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 结束条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
// 获取 mid
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode temp = slow.next;
// 截断左右两部分
slow.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(temp);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummy;
// 合并
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
p.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
p.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = left == null ? right : left;
return dummy.next;
}P146 LRU 缓存
直接使用 LinkedHashMap
java
class LRUCache {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache = new LinkedHashMap<>();
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!cache.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Integer val = cache.get(key);
cache.remove(key);
cache.put(key, val);
return val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (cache.containsKey(key)) {
cache.remove(key);
cache.put(key, value);
return;
}
if (cache.size() + 1 > capacity) {
cache.remove(cache.keySet().iterator().next());
}
cache.put(key, value);
}
}手写双向链表
java
class LRUCache {
class Node {
int key, value;
Node prev, next;
Node(int k, int v) {
key = k;
value = v;
}
}
Node dummy = new Node(0, 0); // 哨兵
HashMap<Integer, Node> cache = new HashMap<>();
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
dummy.prev = dummy;
dummy.next = dummy;
}
// get 流程:
// getNode(key) 会将存在的 Node 调到最前面
// 不存在,返回-1,存在,返回value
public int get(int key) {
Node node = getNode(key);
return node == null ? -1 : node.value;
}
// put 流程
// getNode存在,更新value
// 不存在,创建node,加入map,pushFront
// 插入后超过容量,需要删除尾节点及map中的key
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = getNode(key);
if (node != null) {
node.value = value;
return;
}
node = new Node(key, value);
cache.put(key, node);
pushFront(node);
if (capacity < cache.size()) {
Node backNode = dummy.prev;
remove(backNode);
cache.remove(backNode.key);
}
}
// 将key对应的Node调到最前面,先remove再pushFront
private Node getNode(int key) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node != null) {
remove(node);
pushFront(node);
}
return node;
}
private void pushFront(Node node) {
node.prev = dummy;
node.next = dummy.next;
dummy.next.prev = node;
dummy.next = node;
}
private void remove(Node node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
}P114 二叉树展开为链表
java
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.left != null){
TreeNode next = cur.left;
TreeNode pre = next;
while(pre.right != null){
pre = pre.right;
}
pre.right = cur.right;
cur.left = null;
cur.right = next;
}
cur = cur.right;
}
}P105 前序和后序遍历构造二叉树
java
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return buildTree(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, 0);
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int preIndexLeft, int preIndexRight, int inLeft) {
if (preIndexLeft > preIndexRight) return null;
int cur = preorder[preIndexLeft];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(cur);
int inIndex = map.get(cur);
int sizeLeft = inIndex - inLeft;
root.left = buildTree(preorder, preIndexLeft + 1, preIndexLeft + sizeLeft, inLeft);
root.right = buildTree(preorder, preIndexLeft + sizeLeft + 1, preIndexRight, inIndex + 1);
return root;
}